Hubble is Cilium’s observability platform built on top of eBPF for network visibility and monitoring.
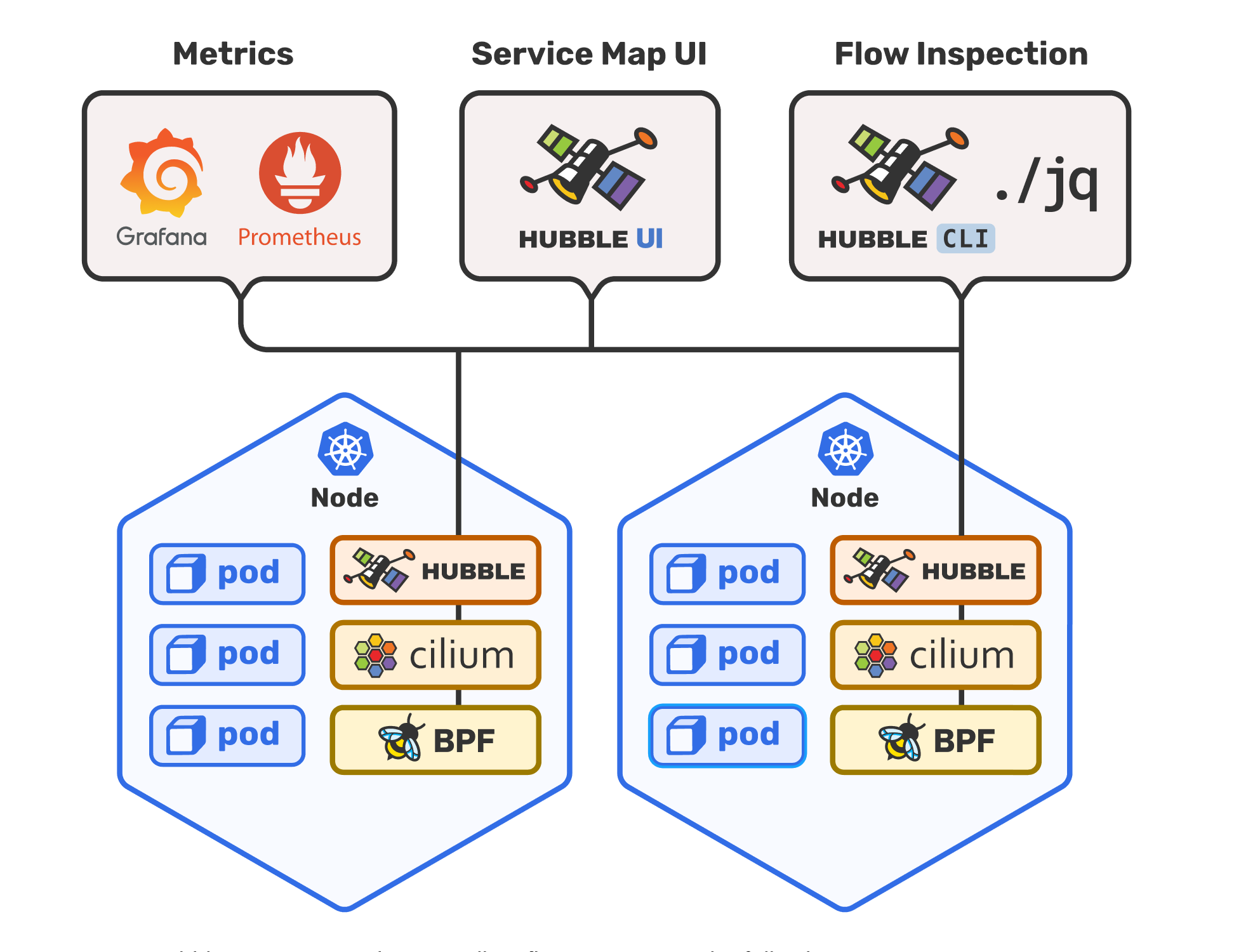
Components Overview
1. Hubble (in Cilium Agent)
Location: Runs inside each Cilium pod (DaemonSet on every node)
Functionality:
- Captures network flows using eBPF at the kernel level
- Monitors all pod-to-pod traffic on that node
- Collects metadata: source/dest IPs, ports, protocols, HTTP methods, DNS queries
- Stores flows in memory (ring buffer)
- Exposes gRPC API on port 4244 for querying flows
What it sees:
| |
2. Hubble Relay
Deployment: Single pod aggregating cluster-wide data
Functionality:
- Aggregates flows from all Cilium agents across all nodes
- Single query endpoint - you query Relay, it queries all nodes
- Provides cluster-wide view of network traffic
- Handles TLS between itself and Cilium agents
- Exposes gRPC API on port 4245
Architecture:
| |
Why it’s needed:
- Without Relay: You’d need to query each node individually
- With Relay: Single query gets flows from entire cluster
3. Hubble UI
Deployment: Single pod with 2 containers
Containers:
- Frontend: Web UI (React app)
- Backend: API server that talks to Hubble Relay
Functionality:
- Visual service map - Shows pods/services as nodes, traffic as edges
- Real-time flow visualization - Green (allowed), red (denied)
- Filtering - By namespace, pod, verdict, protocol
- Flow details - Click on connections to see packet details
- Network policy visualization - See what’s allowed/blocked
What you see:
| |
4. Hubble Services
hubble-peer (ClusterIP:443)
- Used by Hubble Relay to discover Cilium agents
- Peer service for node-to-node communication
hubble-relay (ClusterIP:80)
- Entry point for Hubble CLI and UI
- Aggregates data from all nodes
hubble-ui (ClusterIP:80)
- Web interface access point
- Serves the UI frontend
Data Flow
| |
What Hubble Captures
Layer 3/4
- Source/destination IPs and ports
- Protocols (TCP, UDP, ICMP)
- Packet verdicts (forwarded, dropped, denied)
Layer 7 (Application)
- HTTP: methods, paths, status codes
- DNS: queries and responses
- Kafka: topics and messages
- gRPC: methods and status
Security
- Network policy enforcement
- Identity-based access control
- Dropped/denied connections
Performance
- Latency metrics
- Connection tracking
- Flow rates
Use Cases
1. Troubleshooting
| |
2. Security Monitoring
| |
3. Service Dependencies
| |
4. Compliance
- Network flow logs for auditing
- Policy enforcement verification
- Traffic pattern analysis
Common Commands
| |
Component Summary
| Component | Purpose | You Interact With |
|---|---|---|
| Hubble (in Cilium) | Captures flows on each node | No (automatic) |
| Hubble Relay | Aggregates cluster-wide flows | Via CLI/UI |
| Hubble UI | Visual interface | Yes (browser) |
| hubble CLI | Command-line queries | Yes (terminal) |
Key Benefits
✅ No application changes - eBPF captures at kernel level
✅ Low overhead - Efficient eBPF programs
✅ Real-time - See traffic as it happens
✅ Cluster-wide - Single view across all nodes
✅ Deep visibility - L3-L7 protocol awareness
✅ Security insights - Policy enforcement visibility
✅ Troubleshooting - Debug connectivity issues quickly
Configuration
Current Hubble settings can be viewed with:
| |
Key settings:
enable-hubble: true- Hubble enabledhubble-listen-address: :4244- gRPC API porthubble-disable-tls: false- TLS enabled for security
Summary
Hubble gives you network observability superpowers - see every connection, understand traffic patterns, debug issues, and verify security policies, all without touching your applications! 🔍
